https://sputnikglobe.com/20221001/history-repeats-itself-the-time-us-sabotaged-a-soviet-gas-pipeline-and-bragged-about-it-1101417106.html
History Repeats Itself? The Time US Sabotaged a Soviet Gas Pipeline and Bragged About It
History Repeats Itself? The Time US Sabotaged a Soviet Gas Pipeline and Bragged About It
Sputnik International
Blasts rocked the Nord Stream 1 and 2 natural gas pipelines on Monday, with each pipeline reportedly hit with the force of over 500 kg of TNT – which when... 01.10.2022, Sputnik International
2022-10-01T12:20+0000
2022-10-01T12:20+0000
2023-02-14T12:21+0000
nord stream sabotage
nord stream
soviet union
us
sabotage
explosion
pipeline
virus
https://cdn1.img.sputnikglobe.com/img/07e6/0a/01/1101416521_0:459:2047:1610_1920x0_80_0_0_c06121b3e06f76c324d64f162018a373.jpg
In his address before lawmakers and the nation on Friday on the entry of four new territories into the Russian Federation, Vladimir Putin said that the attacks against Nord Stream were the next logical step for the US and its allies after exhausting anti-Russian sanctions. “It seems incredible but it is a fact – by causing explosions on Nord Stream’s international gas pipelines passing along the bottom of the Baltic Sea, they have actually embarked on the destruction of Europe’s entire energy infrastructure,” the Russian president said.Officials in Denmark, Sweden and Berlin have not ruled out deliberate sabotage, and NATO paid lip service to “support” for “investigations underway to determine the origin of the damage.” A Pentagon official refused to comment on a Flightradar24 analysis showing US military helicopters circling for hours in the areas where the explosions hit prior to the incident. Meanwhile, former Polish Foreign Minister Radoslaw Sikorski tweeted and then deleted a “Thank you, USA” message alongside a picture of a massive methane leak emanating from one of the damaged pipelines, and boasted that “now, $20 billion of scrap metal lies at the bottom of the sea.” Meanwhile, some Western officials and media continue to claim that Russia sabotaged its own pipelines.Everything Old is New AgainThe attacks against Nord Stream are not the first time that a ‘Western trace’ has been suspected in the sabotage of gas pipelines operated by Moscow.In the summer of 1982, the Urengoy-Surgut-Chelyabinsk pipeline carrying natural gas south and west toward Ukraine, where it can be taken further west toward Europe, was rocked by a massive explosion. The explosion’s causes were unknown, and Soviet media never reported on the incident.In 2004, former Reagan special assistant for national security affairs and National Security Council official Thomas Reed published an autobiography entitled ‘At the Abyss’ in which he alleged that the Central Intelligence Agency had sabotaged the pipeline by adding a virus into software the USSR had purchased from a Canadian company to operate the infrastructure.The former official said the act of sabotage was aimed at disrupting the USSR’s gas infrastructure, “its hard currency earnings from the West and the internal Russian economy,” and that the scheme was thought up by National Security Council technology and intelligence advisor Gus Weiss.Portions of the operation were disclosed earlier, in a 1996 paper in CIA journal Studies in Intelligence by Weiss. In it, the former official recalled how, at an economic summit in Ottawa in 1981, French President Francois Mitterrand had informed Ronald Reagan that a KGB double agent named Vladimir Vetrov had come forward to provide French intelligence with 4,000 documents and photographs related to alleged Soviet efforts to get their hands on Western technologies which the US and allies refused to sell due to sanctions and embargoes. The collection of documents was dubbed the ‘Farewell Dossier’.Reed recalled that when the explosion occurred, the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) – the organization tasked with aerospace early warning, initially feared a Soviet “missile liftoff from a place where no rockets were known to be based. Or perhaps it was the detonation of a small nuclear device. Before these conflicting indicators could turn into an international crisis, Gus Weiss came down the hall to tell his fellow National Security Council staffers not to worry.”As has long been the case with the Nord Stream pipelines, the United States had adamantly opposed Soviet projects to deliver gas from Siberia to Western Europe, characterizing them as a means for Moscow to project influence over the Europeans. In 1982, the Reagan administration banned pipeline equipment sales to the USSR, prompting the European Economic Community – forerunner to the European Union, to issue a formal protest over Washington’s interference in the bloc’s economic affairs. Germany, France, Italy and the UK declared the restrictions illegal, and promised to defy the ban. Washington eventually reneged, and the first gas deliveries from Urengoy to Western Europe began in January 1984.To this day, Russian officials have never conceded that the 1982 explosion was the result of CIA interference. In the 1990s and 2000s, when relations between Russia and the US still looked rosy, engineers and ex-KGB agents came forward to tell media that industrial negligence or even shoddy workmanship, and not sabotage, was to blame.The CIA never directly confirmed its involvement in the Urengoy-Surgut-Chelyabinsk pipeline explosion. However, in a page on the CIA’s official website, the agency did boast that “flawed turbines were installed on a gas pipeline” as part of a broader US technological sabotage campaign against the USSR.
https://sputnikglobe.com/20220930/russian-foreign-intel-nord-stream-blasts-are-intl-terrorist-act-with-west-hiding-the-culprits-1101364494.html
https://sputnikglobe.com/20210219/on-a-hair-trigger-soviets-armed-108-jets-for-nuclear-war-during-1983-nato-drills-docs-show-1082132128.html
soviet union
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
2022
News
en_EN
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
nord stream, soviet union, us, sabotage, explosion, pipeline, virus
nord stream, soviet union, us, sabotage, explosion, pipeline, virus
History Repeats Itself? The Time US Sabotaged a Soviet Gas Pipeline and Bragged About It
12:20 GMT 01.10.2022 (Updated: 12:21 GMT 14.02.2023) Blasts rocked the Nord Stream 1 and 2 natural gas pipelines on Monday, with each pipeline reportedly hit with the force of over 500 kg of TNT – which when combined is equivalent to the explosive power of a micro nuke. The Kremlin called the incident an act of terrorism, while Russian intelligence has pointed to a Western trace.
In his address before lawmakers and the nation on Friday on the entry of four new territories into the Russian Federation, Vladimir Putin said that the attacks against Nord Stream were the next logical step for the US and its allies after exhausting anti-Russian sanctions. “It seems incredible but it is a fact – by causing explosions on Nord Stream’s international gas pipelines passing along the bottom of the Baltic Sea, they have actually embarked on the destruction of Europe’s entire energy infrastructure,” the Russian president
said.
Officials in Denmark, Sweden and Berlin have not ruled out deliberate sabotage, and NATO paid lip service to
“support” for “investigations underway to determine the origin of the damage.” A Pentagon official refused to comment on a Flightradar24 analysis showing US military helicopters circling for hours in the areas where the explosions hit prior to the incident. Meanwhile, former Polish Foreign Minister Radoslaw Sikorski
tweeted and then deleted a “Thank you, USA” message alongside a picture of a massive methane leak emanating from one of the damaged pipelines, and boasted that “now, $20 billion of scrap metal lies at the bottom of the sea.” Meanwhile, some Western officials and media continue to claim
that Russia sabotaged its own pipelines.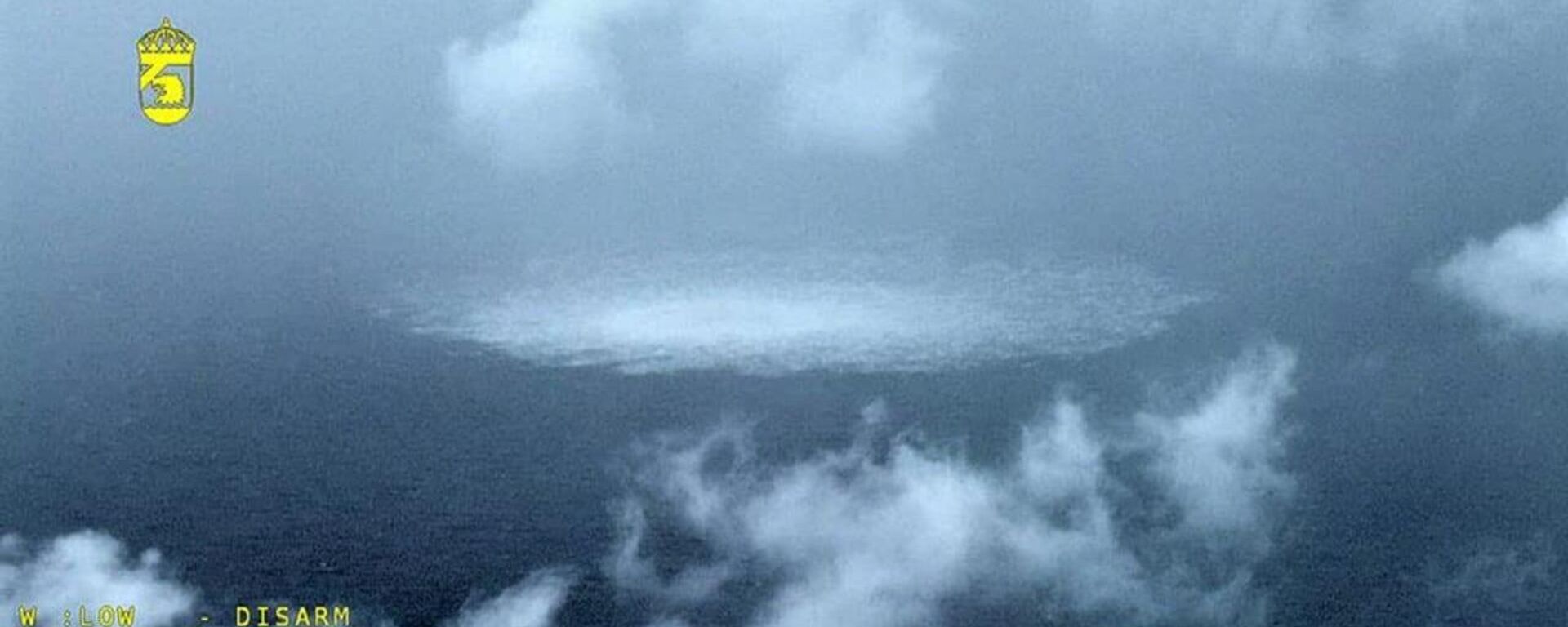
30 September 2022, 07:38 GMT
Everything Old is New Again
The attacks against Nord Stream are not the first time that a ‘Western trace’ has been suspected in the sabotage of gas pipelines operated by Moscow.
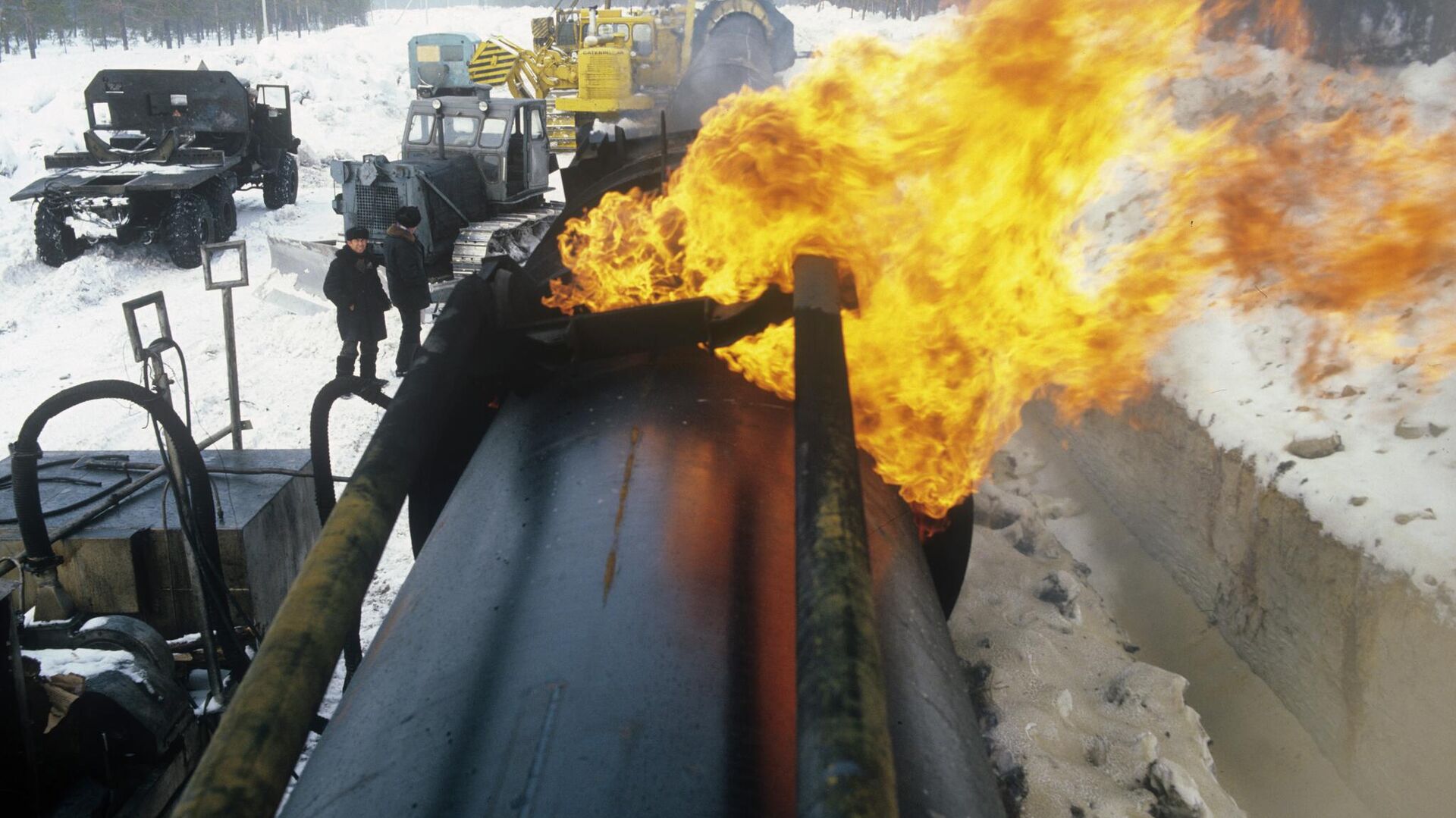
In the summer of 1982, the Urengoy-Surgut-Chelyabinsk pipeline carrying natural gas south and west toward Ukraine, where it can be taken further west toward Europe, was rocked by a massive explosion. The explosion’s causes were unknown, and Soviet media never reported on the incident.
In 2004, former Reagan special assistant for national security affairs and National Security Council official Thomas Reed published an autobiography entitled ‘At the Abyss’ in which he alleged that the Central Intelligence Agency had sabotaged the pipeline by adding a virus into software the USSR had purchased from a Canadian company to operate the infrastructure.
“The pipeline software that was to run the pumps, turbines and valves was programmed to go haywire, to reset pump speeds and valve settings to produce pressures far beyond those acceptable to the pipeline joints and welds. The result was the most monumental non-nuclear explosion and fire ever seen from space,” Reed
recalled.
The former official said the act of sabotage was aimed at disrupting the USSR’s gas infrastructure, “its hard currency earnings from the West and the internal Russian economy,” and that the scheme was thought up by National Security Council technology and intelligence advisor Gus Weiss.
Portions of the operation were disclosed earlier, in a 1996 paper in CIA journal Studies in Intelligence by Weiss. In it, the former official recalled how, at an economic summit in Ottawa in 1981, French President Francois Mitterrand had informed Ronald Reagan that a KGB double agent named Vladimir Vetrov had come forward to provide French intelligence with 4,000 documents and photographs related to alleged Soviet efforts to get their hands on Western technologies which the US and allies refused to sell due to sanctions and embargoes. The collection of documents was dubbed
the ‘Farewell Dossier’.In January 1982, Weiss said, he proposed the pipeline sabotage idea to CIA director William Casey. “Reagan received the plan enthusiastically” and “Casey was given a go,” Reed wrote in his account.
Reed recalled that when the explosion occurred, the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) – the organization tasked with aerospace early warning, initially feared a Soviet “missile liftoff from a place where no rockets were known to be based. Or perhaps it was the detonation of a small nuclear device. Before these conflicting indicators could turn into an international crisis, Gus Weiss came down the hall to tell his fellow National Security Council staffers not to worry.”
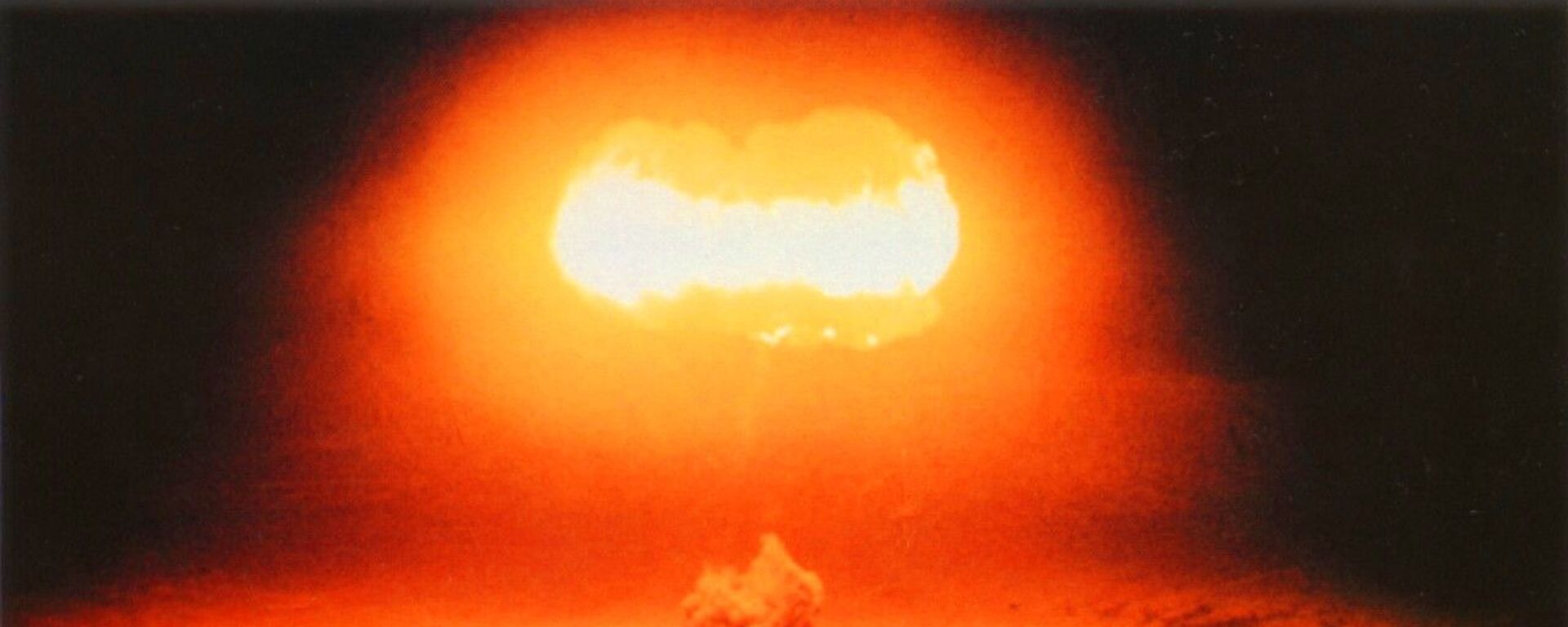
19 February 2021, 22:31 GMT
As has long been the case with the Nord Stream pipelines, the United States had adamantly opposed Soviet projects to deliver gas from Siberia to Western Europe, characterizing them as a means for Moscow to project influence over the Europeans. In 1982, the Reagan administration
banned pipeline equipment sales to the USSR, prompting the European Economic Community – forerunner to the European Union, to issue a formal protest over Washington’s interference in the bloc’s economic affairs. Germany, France, Italy and the UK declared the restrictions illegal, and promised to defy the ban. Washington eventually reneged, and the first gas deliveries from Urengoy to Western Europe
began in January 1984.
To this day, Russian officials have never conceded that the 1982 explosion was the result of CIA interference. In the 1990s and 2000s, when relations between Russia and the US still looked rosy, engineers and ex-KGB agents
came forward to tell media that industrial negligence or even
shoddy workmanship, and not sabotage, was to blame.
The CIA never directly confirmed its involvement in the Urengoy-Surgut-Chelyabinsk pipeline explosion. However, in a
page on the CIA’s official website, the agency did boast that “flawed turbines were installed on a gas pipeline” as part of a broader US technological sabotage campaign against the USSR.








